When connected full time to a GPS...
- provides real time tracking ability – OziExplorer can plot your position directly onto the map on the screen, this is called "Moving Map". You have a calibrated map available which covers the position the GPS is sending.
- Will work with any GPS which sends NMEA 0183 sentences $GPRMC or ($GPGGA and $GPVTG) or ($GPGLL and $GPVTG).
- automatically changes to the next map when your position moves off the current map or across the map "neat lines". The "neat lines" (corner markers) are set up in "Check Map Calibration".
- auto search for a more detailed map – OziExplorer can be set to scan for more detailed maps at configured intervals and load a more detailed map if one is available. (Note - you do not have to cross the map "neat line" for this to occur).
Ability to show the track onscreen and log it direct to a file.
- The track can be plotted on screen as you move (like a "bread crumb" trail).
- You can set the length of the track to be displayed or you can display all the track points collected.
- You can set the interval the track point updates in distance units (Kilometers, Miles or Nautical Miles), or how often a track point is collected.
- Vary the screen update rate; the track points are collected but update the screen less frequently. Specify an update rate of a few seconds or more to reduce flickering on slower laptops.
- The track can be logged direct to a file. This track file can be loaded and displayed on a map.
Choice of pointer graphic or make your own
- Select the pointer graphic (shape) to show your moving map position.
- 8 built-in graphics.
- 3 user defined graphics to make your own pointer shape.
- Change the size of the pointer seen on screen and the color that is the best color for your maps.
- The pointer can be drawn a solid color or transparent (you can see map details through the pointer).
Display speed, altitude and bearing.
- Several parameters can be displayed as you move in a special moving map window.
- speed in the speed units you specify.
- altitude in the units you specify.
- direction of travel (bearing), True North and Magnetic North.
Navigate to a Waypoint or navigate along a predefined Route
- As well as using the moving map feature of OziExplorer to display your actual position on a map as you move, you can use the Navigation feature to help you navigate to a waypoint or along a route composed of waypoints.
- A Navigation Control shows you the information you need to navigate to the waypoint or to the 1st waypoint in a route.
- Show the name of the next waypoint.
- The distance to the next waypoint.
- Course to Steer, the bearing to steer for a straight course to the waypoint.
- Cross Track Error, your deviation from the desired course line.
- Estimated time enroute (ETE), how long to get to the next waypoint from your current position.
- Estimated time of arrival (ETA), the time of your arrival at the next waypoint.
- If navigating along a route, the total ETE and ETA estimate can be displayed.
- Project a line from your current position along your current course. You can configure the line thickness and color. You can also draw a line from your current position to the next waypoint.
- Set a proximity around the waypoint. The software determines if you have reached a waypoint by:
- Entering the Route Wp proximity zone.
- Going past the waypoint, a line perpendicular to the leg direction (eg. for marine use).
Sound and show alarms when approaching waypoints.
- Set the length of time the alarms will sound for (in seconds) when the proximity is entered or the proximity is reached, setting to 0 will turn off the alarm sound. Alarms include:
- Approaching any waypoint which has a proximity set within its proximity.
- Approaching the active waypoint in the active route.
- You have traveled to or past the next (active) waypoint in the active route.
- You have reached the end of the route.
- You have entered an Alarm Zone.
Sound and show alarms when entering Alarm Zones
- Alarm Zones are polygons (multi sided boxes) drawn onto the map, if you travel into (enter) into an alarm zone while in moving map mode an alarm will sound.
- Alarm zones are mainly used in the marine environment to mark reefs etc but may have uses elsewhere.
- Alarm Zones are attached to the map and automatically loaded when the map is loaded. Up to 50 tracks and alarm zones can be attached.
- Up to 100 points can be used to form an alarm zone.
Display Range Rings or a Compass Rose at the GPS position
- You can turn on "Range Rings", circles drawn around the current GPS position (using moving map).
- The radius, number of rings, color and width of the rings can be specified.
- You can have a "Compass Rose" displayed around your present position when using "moving map", the compass can be configured for:
- the direction that zero degrees on the compass points, true north, magnetic north or course.
- the color and width of the circle lines and tick marks which make up to compass.
Three mode settings for Night Vision
- Turns all screen colors into shades of red, gray or blue for better vision at night.
Set screen intensity
- Allows you to set the intensity of the screen colors to reduce the brightness of the screen at night.
Show your position in a separate Regional Map window
- The regional map window is used when using moving map (real time tracking) mode, it shows your position on a map loaded in the regional map window.
Anchor Alarm
- The Anchor Alarm will check how far your vessel has drifted from its anchor point and sound an alarm when the value exceeds the specified radius. You can display the track (movement history) in the Anchor Alarm window as the vessel moves. Make your own sound file to play when the vessel moves outside the defined radius.
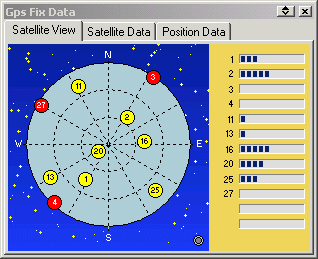
Satellite View and GPS Fix Information
- The graphical display shows the satellites your GPS has connected with.
- The bar graph shows the signal level (SNR) of the satellites in view.
- Other information displayed is:
- Fix Quality.
- Number of Satellites the GPS is tracking.
- Horizontal Dilution of Precision.
- Time in seconds since the last DGPS update.
- DGPS Station number being used.
- The position data of the current position from the NMEA sentences.
- Speed.
- Altitude.
- Course heading.